Multi-Fidelity Kriging (MFK)¶
MFK is a multi-fidelity modeling method which uses an autoregressive model of order 1 (AR1).
where \(\rho(x)\) is a scaling/correlation factor (constant, linear or quadratic) and \(\delta(\cdot)\) is a discrepancy function.
The additive AR1 formulation was first introduced by Kennedy and O’Hagan [1]. The implementation here follows the one proposed by Le Gratiet [2]. It offers the advantage of being recursive, easily extended to \(n\) levels of fidelity and offers better scaling for high numbers of samples. This method only uses nested sampling training points as described by Le Gratiet [2].
References¶
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.applications.mfk import MFK, NestedLHS
# low fidelity model
def lf_function(x):
import numpy as np
return (
0.5 * ((x * 6 - 2) ** 2) * np.sin((x * 6 - 2) * 2)
+ (x - 0.5) * 10.0
- 5
)
# high fidelity model
def hf_function(x):
import numpy as np
return ((x * 6 - 2) ** 2) * np.sin((x * 6 - 2) * 2)
# Problem set up
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 1.0]])
xdoes = NestedLHS(nlevel=2, xlimits=xlimits, random_state=0)
xt_c, xt_e = xdoes(7)
# Evaluate the HF and LF functions
yt_e = hf_function(xt_e)
yt_c = lf_function(xt_c)
sm = MFK(theta0=xt_e.shape[1] * [1.0])
# low-fidelity dataset names being integers from 0 to level-1
sm.set_training_values(xt_c, yt_c, name=0)
# high-fidelity dataset without name
sm.set_training_values(xt_e, yt_e)
# train the model
sm.train()
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 101, endpoint=True).reshape(-1, 1)
# query the outputs
y = sm.predict_values(x)
_mse = sm.predict_variances(x)
_derivs = sm.predict_derivatives(x, kx=0)
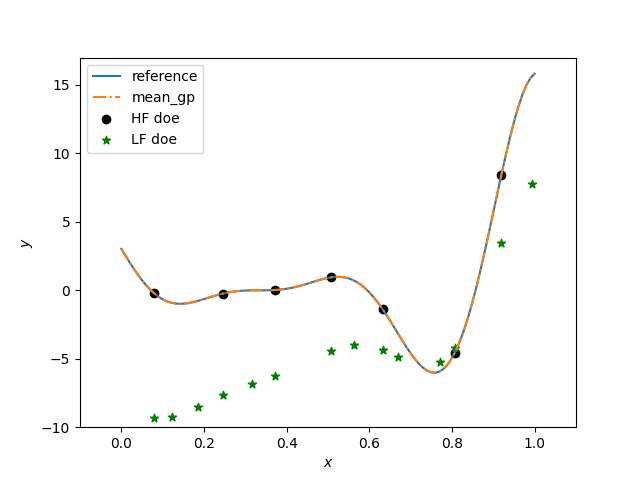
plt.figure()
plt.plot(x, hf_function(x), label="reference")
plt.plot(x, y, linestyle="-.", label="mean_gp")
plt.scatter(xt_e, yt_e, marker="o", color="k", label="HF doe")
plt.scatter(xt_c, yt_c, marker="*", color="g", label="LF doe")
plt.legend(loc=0)
plt.ylim(-10, 17)
plt.xlim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.xlabel(r"$x$")
plt.ylabel(r"$y$")
plt.show()
___________________________________________________________________________
MFK
___________________________________________________________________________
Problem size
# training points. : 7
___________________________________________________________________________
Training
Training ...
Training - done. Time (sec): 0.4344051
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 101
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0002229
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000022
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 101
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0001872
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000019
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
print_global |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Global print toggle. If False, all printing is suppressed |
print_training |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print training information |
print_prediction |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print prediction information |
print_problem |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print problem information |
print_solver |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print solver information |
poly |
constant |
[‘constant’, ‘linear’, ‘quadratic’] |
[‘str’] |
Regression function type |
corr |
squar_exp |
[‘pow_exp’, ‘abs_exp’, ‘squar_exp’, ‘act_exp’, ‘matern52’, ‘matern32’] |
None |
Correlation function type |
pow_exp_power |
1.9 |
None |
[‘float’] |
Power for the pow_exp kernel function (valid values in (0.0, 2.0]), This option is set automatically when corr option is squar, abs, or matern. |
categorical_kernel |
MixIntKernelType.CONT_RELAX |
[<MixIntKernelType.CONT_RELAX: ‘CONT_RELAX’>, <MixIntKernelType.GOWER: ‘GOWER’>, <MixIntKernelType.EXP_HOMO_HSPHERE: ‘EXP_HOMO_HSPHERE’>, <MixIntKernelType.HOMO_HSPHERE: ‘HOMO_HSPHERE’>, <MixIntKernelType.COMPOUND_SYMMETRY: ‘COMPOUND_SYMMETRY’>] |
None |
The kernel to use for categorical inputs. Only for non continuous Kriging |
hierarchical_kernel |
MixHrcKernelType.ALG_KERNEL |
[<MixHrcKernelType.ALG_KERNEL: ‘ALG_KERNEL’>, <MixHrcKernelType.ARC_KERNEL: ‘ARC_KERNEL’>] |
None |
The kernel to use for mixed hierarchical inputs. Only for non continuous Kriging |
nugget |
2.220446049250313e-14 |
None |
[‘float’] |
a jitter for numerical stability |
theta0 |
[0.01] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
Initial hyperparameters |
theta_bounds |
[1e-06, 20.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
bounds for hyperparameters |
hyper_opt |
TNC |
[‘Cobyla’, ‘TNC’] |
[‘str’] |
Optimiser for hyperparameters optimisation |
eval_noise |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
noise evaluation flag |
noise0 |
[0.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
Initial noise hyperparameters |
noise_bounds |
[2.220446049250313e-14, 10000000000.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
bounds for noise hyperparameters |
use_het_noise |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
heteroscedastic noise evaluation flag |
n_start |
10 |
None |
[‘int’] |
number of optimizer runs (multistart method) |
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
definition of a design space of float (continuous) variables: array-like of size nx x 2 (lower, upper bounds) |
design_space |
None |
None |
[‘BaseDesignSpace’, ‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
definition of the (hierarchical) design space: use smt.utils.design_space.DesignSpace as the main API. Also accepts list of float variable bounds |
random_state |
41 |
None |
[‘NoneType’, ‘int’, ‘RandomState’] |
Numpy RandomState object or seed number which controls random draws for internal optim (set by default to get reproductibility) |
rho_regr |
constant |
[‘constant’, ‘linear’, ‘quadratic’] |
None |
Regression function type for rho |
optim_var |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
If True, the variance at HF samples is forced to zero |
propagate_uncertainty |
True |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
If True, the variance cotribution of lower fidelity levels are considered |