KPLSK¶
KPLSK is a KPLS-based model and is basically built in two steps. The first step consists in running KPLS and giving the estimate hyperparameters expressed in the reduced space with a number of dimensions equals to \(h\). The second step consists in expressing the estimate hyperparameters in the original space with a number of dimensions equals to \(nx\), and then using it as a starting point to locally optimizing the likelihood function of a standard kriging. The idea here is guessing a “good” initial hyperparameters and applying a gradient-based optimization using a classic kriging-kernels. The “good” guess will be provided by KPLS: the solutions \(\left(\theta_1^*,\dots,\theta_h^*\right)\) and the PLS-coefficients \(\left(w_1^{(k)},\dots,w_{nx}^{(k)}\right)\) for \(k=1,\dots,h\). By a change of variables \(\eta_l=\sum_{k=1}^h\theta_k^*{w^{(k)}_l}^2\), for \(l=1,\dots,nx\), we can express the initial hyperparameters point in the original space. In the following example, a KPLS-Gaussian kernel function \(k_{\text{KPLS}}\) is used for the demonstration (More details are given in [1]):
\(\prod\limits_{l=1}^{nx}\exp\left(-\eta_l\left(x_l^{(i)}-x_l^{(j)}\right)^2\right)\) is a standard Gaussian kernel function.
Subsequently, the hyperparameters point \(\left(\eta_1=\sum_{k=1}^h\theta_k^*{w^{(k)}_1}^2,\dots,\eta_{nx}=\sum_{k=1}^h\theta_k^*{w^{(k)}_{nx}}^2\right)\) is used as a starting point for a gradient-based optimization applied on a standard kriging method.
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.surrogate_models import KPLSK
xt = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0])
yt = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 1.5, 0.9, 1.0])
sm = KPLSK(theta0=[1e-2])
sm.set_training_values(xt, yt)
sm.train()
num = 100
x = np.linspace(0.0, 4.0, num)
y = sm.predict_values(x)
# estimated variance
s2 = sm.predict_variances(x)
# derivative according to the first variable
_dydx = sm.predict_derivatives(xt, 0)
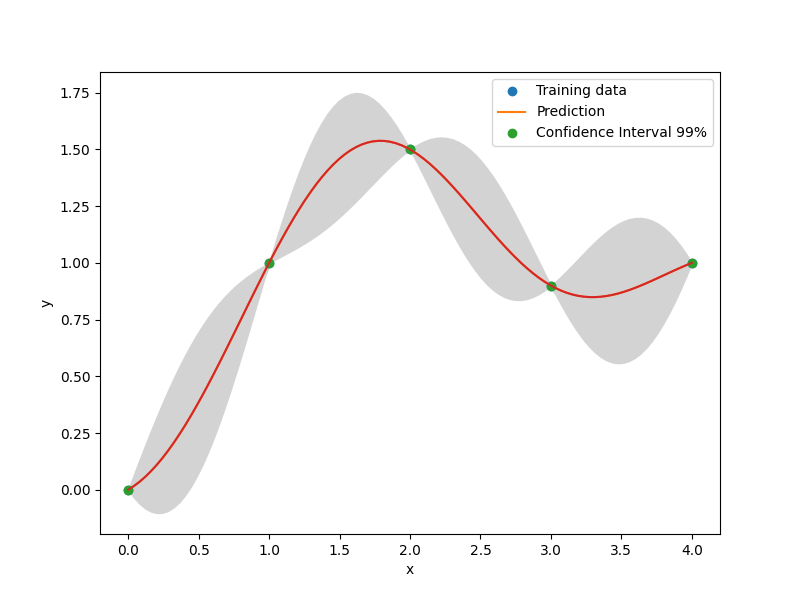
plt.plot(xt, yt, "o")
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.legend(["Training data", "Prediction"])
plt.show()
# add a plot with variance
plt.plot(xt, yt, "o")
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.fill_between(
np.ravel(x),
np.ravel(y - 3 * np.sqrt(s2)),
np.ravel(y + 3 * np.sqrt(s2)),
color="lightgrey",
)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.legend(["Training data", "Prediction", "Confidence Interval 99%"])
plt.show()
___________________________________________________________________________
KPLSK
___________________________________________________________________________
Problem size
# training points. : 5
___________________________________________________________________________
Training
Training ...
Training - done. Time (sec): 0.2184792
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 100
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0009468
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000095
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 5
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0001400
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000280
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
print_global |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Global print toggle. If False, all printing is suppressed |
print_training |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print training information |
print_prediction |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print prediction information |
print_problem |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print problem information |
print_solver |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print solver information |
poly |
constant |
[‘constant’, ‘linear’, ‘quadratic’] |
[‘str’] |
Regression function type |
corr |
squar_exp |
[‘squar_exp’] |
[‘str’] |
Correlation function type |
pow_exp_power |
1.9 |
None |
[‘float’] |
Power for the pow_exp kernel function (valid values in (0.0, 2.0]), This option is set automatically when corr option is squar, abs, or matern. |
categorical_kernel |
MixIntKernelType.CONT_RELAX |
[<MixIntKernelType.CONT_RELAX: ‘CONT_RELAX’>, <MixIntKernelType.GOWER: ‘GOWER’>, <MixIntKernelType.EXP_HOMO_HSPHERE: ‘EXP_HOMO_HSPHERE’>, <MixIntKernelType.HOMO_HSPHERE: ‘HOMO_HSPHERE’>, <MixIntKernelType.COMPOUND_SYMMETRY: ‘COMPOUND_SYMMETRY’>] |
None |
The kernel to use for categorical inputs. Only for non continuous Kriging |
hierarchical_kernel |
MixHrcKernelType.ALG_KERNEL |
[<MixHrcKernelType.ALG_KERNEL: ‘ALG_KERNEL’>, <MixHrcKernelType.ARC_KERNEL: ‘ARC_KERNEL’>] |
None |
The kernel to use for mixed hierarchical inputs. Only for non continuous Kriging |
nugget |
2.220446049250313e-14 |
None |
[‘float’] |
a jitter for numerical stability |
theta0 |
[0.01] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
Initial hyperparameters |
theta_bounds |
[1e-06, 20.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
bounds for hyperparameters |
hyper_opt |
TNC |
[‘Cobyla’, ‘TNC’] |
[‘str’] |
Optimiser for hyperparameters optimisation |
eval_noise |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
noise evaluation flag |
noise0 |
[0.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
Initial noise hyperparameters |
noise_bounds |
[2.220446049250313e-14, 10000000000.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
bounds for noise hyperparameters |
use_het_noise |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
heteroscedastic noise evaluation flag |
n_start |
10 |
None |
[‘int’] |
number of optimizer runs (multistart method) |
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
definition of a design space of float (continuous) variables: array-like of size nx x 2 (lower, upper bounds) |
design_space |
None |
None |
[‘BaseDesignSpace’, ‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
definition of the (hierarchical) design space: use smt.utils.design_space.DesignSpace as the main API. Also accepts list of float variable bounds |
random_state |
41 |
None |
[‘NoneType’, ‘int’, ‘RandomState’] |
Numpy RandomState object or seed number which controls random draws for internal optim (set by default to get reproductibility) |
n_comp |
1 |
None |
[‘int’] |
Number of principal components |
eval_n_comp |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
n_comp evaluation flag |
eval_comp_treshold |
1.0 |
None |
[‘float’] |
n_comp evaluation treshold for Wold’s R criterion |
cat_kernel_comps |
None |
None |
[‘list’] |
Number of components for PLS categorical kernel |