Variable-fidelity modeling (VFM)¶
VFM is a variable-fidelity modeling method which can use additive, multiplicative, or hybride bridge functions. SMT proposes only additive and multiplicative options.
In the additive method, high- and low-fidelity models, \(y_{\text{high}}({\bf x})\) and \(y_{\text{low}}({\bf x})\), are calibrated by adding the low-fidelity model to a function \(\gamma({\bf x})\), also called bridge function
The additive bridge function was developed by Lewis and Nash [1].
In the same way, the multiplicative bridge function is defined by
However, the multiplicative bridge function may cause problems when one of the sampled values of the low-fidelity model is close to zero.
After the unknown bridge function \(\gamma\) and low-fidelity model \(y_\text{low}\) have been approximated with \(\hat{\gamma}\) and \(\hat{y}_\text{low}\), respectively, the response of the high-fidelity model is obtained
Usage¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from smt.problems import WaterFlowLFidelity, WaterFlow
from smt.sampling_methods import LHS
from smt.applications import VFM
# Problem set up
ndim = 8
ntest = 500
ndoeLF = int(10 * ndim)
ndoeHF = int(3)
funLF = WaterFlowLFidelity(ndim=ndim)
funHF = WaterFlow(ndim=ndim)
deriv1 = True
deriv2 = True
LF_candidate = "QP"
Bridge_candidate = "KRG"
type_bridge = "Multiplicative"
optionsLF = {}
optionsB = {
"theta0": [1e-2] * ndim,
"print_prediction": False,
"deriv": False,
"hyper_opt": "Cobyla",
}
# Construct low/high fidelity data and validation points
sampling = LHS(xlimits=funLF.xlimits, criterion="m")
xLF = sampling(ndoeLF)
yLF = funLF(xLF)
if deriv1:
dy_LF = np.zeros((ndoeLF, 1))
for i in range(ndim):
yd = funLF(xLF, kx=i)
dy_LF = np.concatenate((dy_LF, yd), axis=1)
sampling = LHS(xlimits=funHF.xlimits, criterion="m")
xHF = sampling(ndoeHF)
yHF = funHF(xHF)
if deriv2:
dy_HF = np.zeros((ndoeHF, 1))
for i in range(ndim):
yd = funHF(xHF, kx=i)
dy_HF = np.concatenate((dy_HF, yd), axis=1)
xtest = sampling(ntest)
ytest = funHF(xtest)
dytest = np.zeros((ntest, ndim))
for i in range(ndim):
dytest[:, i] = funHF(xtest, kx=i).T
# Initialize the extension VFM
M = VFM(
type_bridge=type_bridge,
name_model_LF=LF_candidate,
name_model_bridge=Bridge_candidate,
X_LF=xLF,
y_LF=yLF,
X_HF=xHF,
y_HF=yHF,
options_LF=optionsLF,
options_bridge=optionsB,
dy_LF=dy_LF,
dy_HF=dy_HF,
)
# Prediction of the validation points
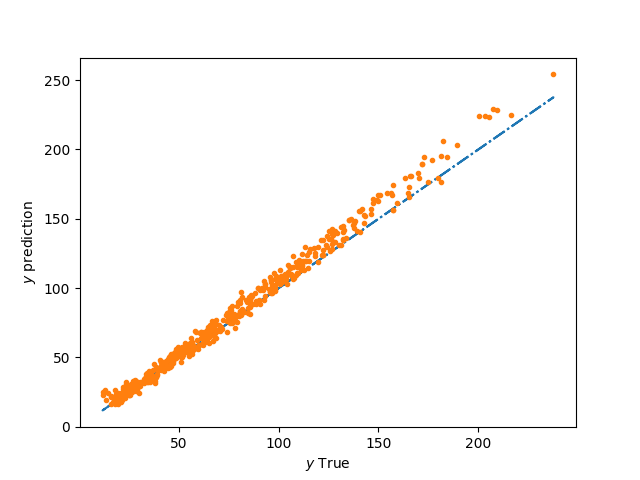
y = M.predict_values(x=xtest)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(ytest, ytest, "-.")
plt.plot(ytest, y, ".")
plt.xlabel(r"$y$ True")
plt.ylabel(r"$y$ prediction")
plt.show()
___________________________________________________________________________
Kriging
___________________________________________________________________________
Problem size
# training points. : 3
___________________________________________________________________________
Training
Training ...
Training - done. Time (sec): 0.1210840
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
name_model_LF |
None |
[‘KRG’, ‘LS’, ‘QP’, ‘KPLS’, ‘KPLSK’, ‘GEKPLS’, ‘RBF’, ‘RMTC’, ‘RMTB’, ‘IDW’] |
[‘object’] |
Name of the low-fidelity model |
options_LF |
{} |
None |
[‘dict’] |
Options for the low-fidelity model |
name_model_bridge |
None |
[‘KRG’, ‘LS’, ‘QP’, ‘KPLS’, ‘KPLSK’, ‘GEKPLS’, ‘RBF’, ‘RMTC’, ‘RMTB’, ‘IDW’] |
[‘object’] |
Name of the bridge model |
options_bridge |
{} |
None |
[‘dict’] |
Options for the bridge model |
type_bridge |
Additive |
[‘Additive’, ‘Multiplicative’] |
[‘str’] |
Bridge function type |
X_LF |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
Low-fidelity inputs |
y_LF |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
Low-fidelity output |
X_HF |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
High-fidelity inputs |
y_HF |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
High-fidelity output |
dy_LF |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
Low-fidelity derivatives |
dy_HF |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
High-fidelity derivatives |