Sampling methods¶
SMT contains a library of sampling methods used to generate sets of points in the input space, either for training or for prediction. These are listed below.
Usage¶
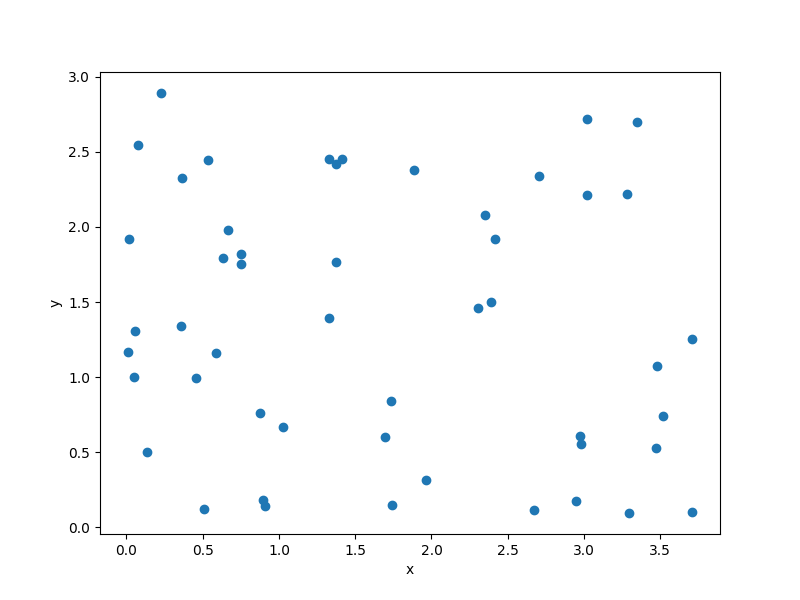
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.sampling_methods import Random
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 4.0], [0.0, 3.0]])
sampling = Random(xlimits=xlimits)
num = 50
x = sampling(num)
print(x.shape)
plt.plot(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], "o")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.show()
(50, 2)
Sampling method class API¶
- class smt.sampling_methods.sampling_method.SamplingMethod(**kwargs)[source]¶
Methods
__call__([nt])Compute the samples.
- __init__(**kwargs)[source]¶
Constructor where values of options can be passed in. xlimits keyword argument is required.
For the list of options, see the documentation for the sampling method being used.
- Parameters:
- **kwargsnamed arguments
Set of options that can be optionally set; each option must have been declared.
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from smt.sampling_methods import Random >>> sampling = Random(xlimits=np.arange(2).reshape((1, 2)))
- __call__(nt: int = None) ndarray[source]¶
Compute the samples. Depending on the concrete sampling method the requested number of samples nt may not be enforced.
The number of dimensions (nx) is determined based on xlimits.shape[0].
- Parameters:
- ntint
Number of points hint.
- Returns:
- ndarray[nt, nx]
The sampling locations in the input space.