pyDOE sampling methods¶
pyDOE is a package for design of experiments [1] (LHS implementation in SMT is based on pyDOE LHS).
Main DOE functions provided by pyDOE are made available through an adapter base class PyDoeSamplingMethod which makes them compliant with the SamplingMethod base class interface.
While historically the sampling method interface of SMT requires to specify a number of points, pyDOE design methods output a number of points which is only determined by the dimension of x and other method-specific options.
The following designs are exposed:
Box Behnken design
Plackett-Burman design
Factorial design
Generalized Subset Design
See pyDOE3 documentation [2]
References
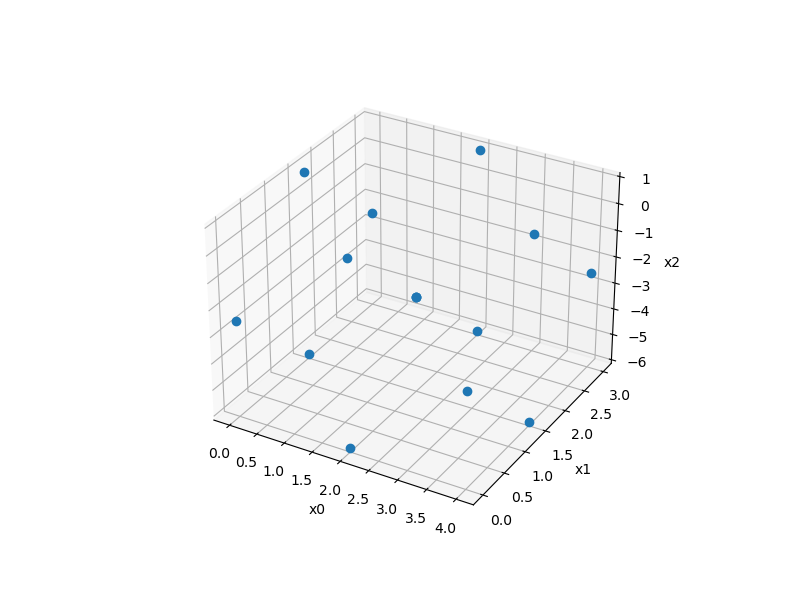
Box Behnken sampling¶
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.sampling_methods import BoxBehnken
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 4.0], [0.0, 3.0], [-6.0, 1.0]])
sampling = BoxBehnken(xlimits=xlimits)
x = sampling()
print(x.shape)
ax = plt.axes(projection="3d")
ax.plot3D(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], x[:, 2], "o")
ax.set_xlabel("x0")
ax.set_ylabel("x1")
ax.set_zlabel("x2")
plt.show()
(15, 3)
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
The interval of the domain in each dimension with shape nx x 2 (required) |
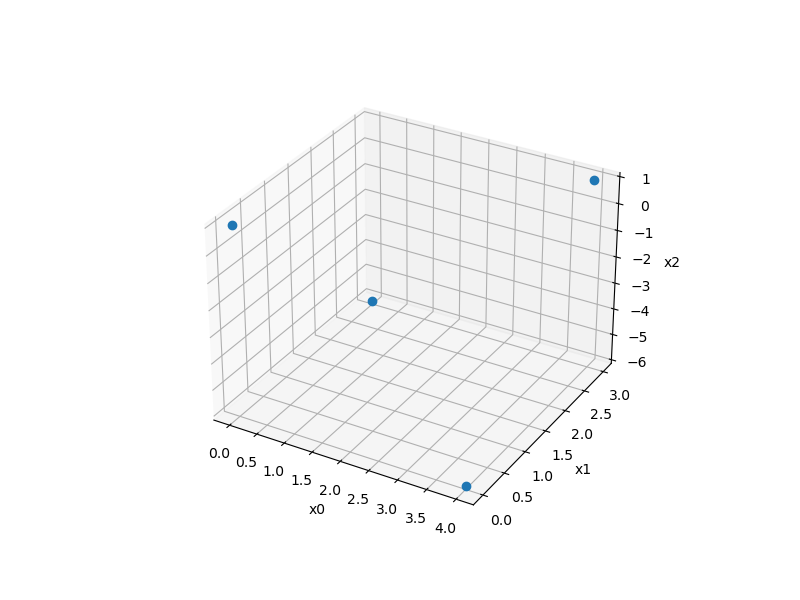
Plackett-Burman sampling¶
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.sampling_methods import PlackettBurman
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 4.0], [0.0, 3.0], [-6.0, 1.0]])
sampling = PlackettBurman(xlimits=xlimits)
x = sampling()
print(x.shape)
ax = plt.axes(projection="3d")
ax.plot3D(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], x[:, 2], "o")
ax.set_xlabel("x0")
ax.set_ylabel("x1")
ax.set_zlabel("x2")
plt.show()
(4, 3)
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
The interval of the domain in each dimension with shape nx x 2 (required) |
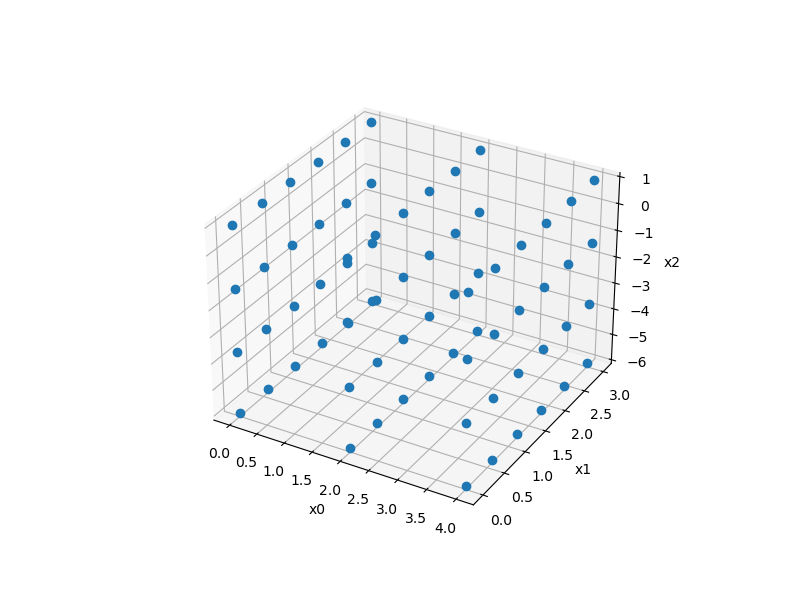
Factorial sampling¶
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.sampling_methods import Factorial
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 4.0], [0.0, 3.0], [-6.0, 1.0]])
sampling = Factorial(xlimits=xlimits, levels=[3, 6, 4])
x = sampling()
print(x.shape)
ax = plt.axes(projection="3d")
ax.plot3D(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], x[:, 2], "o")
ax.set_xlabel("x0")
ax.set_ylabel("x1")
ax.set_zlabel("x2")
plt.show()
(72, 3)
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
The interval of the domain in each dimension with shape nx x 2 (required) |
levels |
None |
None |
[‘list’] |
number of factor levels per factor in design |
Generalized Subset sampling¶
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.sampling_methods import Gsd
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 4.0], [0.0, 3.0], [-6.0, 1.0]])
sampling = Gsd(xlimits=xlimits, levels=[3, 6, 4])
x = sampling()
print(x.shape)
ax = plt.axes(projection="3d")
ax.plot3D(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], x[:, 2], "o")
ax.set_xlabel("x0")
ax.set_ylabel("x1")
ax.set_zlabel("x2")
plt.show()
(36, 3)
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘ndarray’] |
The interval of the domain in each dimension with shape nx x 2 (required) |
levels |
None |
None |
[‘list’] |
number of factor levels per factor in design |
reduction |
2 |
None |
[‘int’] |
Reduction factor (bigger than 1). Larger reduction means fewer experiments in the design and more possible complementary designs |