Multi-Fidelity Kriging KPLS (MFKPLS)¶
Partial Least Squares (PLS) is a statistical method to analyze the variations of a quantity of interest w.r.t underlying variables. PLS method gives directions (principal compoenents) that maximize the variation of the quantity of interest.
These principal components define rotations that can be applied to define bases changes. The principal components can be truncated at any number (called n_comp) to explain a ’majority’ of the data variations. [1] used the PLS to define subspaces to make high-dimensional Kriging more efficient.
We apply the same idea to Multi-Fidelity Kriging (MFK). The only difference is that we do not apply the PLS analysis step on all datasets. We apply the PLS analysis step on the high-fidelity to preserve the robustness to poor correlations between fidelity levels. A hyperparameter optimization is then performed in the subspace that maximizes the variations of HF data.
MFKPLS is a combination of Multi-Fidelity Kriging (MFK) and KPLS techniques.
References¶
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.applications.mfk import NestedLHS
from smt.applications.mfkpls import MFKPLS
# low fidelity model
def lf_function(x):
import numpy as np
return (
0.5 * ((x * 6 - 2) ** 2) * np.sin((x * 6 - 2) * 2)
+ (x - 0.5) * 10.0
- 5
)
# high fidelity model
def hf_function(x):
import numpy as np
return ((x * 6 - 2) ** 2) * np.sin((x * 6 - 2) * 2)
# Problem set up
xlimits = np.array([[0.0, 1.0]])
xdoes = NestedLHS(nlevel=2, xlimits=xlimits, random_state=0)
xt_c, xt_e = xdoes(7)
# Evaluate the HF and LF functions
yt_e = hf_function(xt_e)
yt_c = lf_function(xt_c)
# choice of number of PLS components
ncomp = 1
sm = MFKPLS(n_comp=ncomp, theta0=ncomp * [1.0])
# low-fidelity dataset names being integers from 0 to level-1
sm.set_training_values(xt_c, yt_c, name=0)
# high-fidelity dataset without name
sm.set_training_values(xt_e, yt_e)
# train the model
sm.train()
x = np.linspace(0, 1, 101, endpoint=True).reshape(-1, 1)
# query the outputs
y = sm.predict_values(x)
_mse = sm.predict_variances(x)
_derivs = sm.predict_derivatives(x, kx=0)
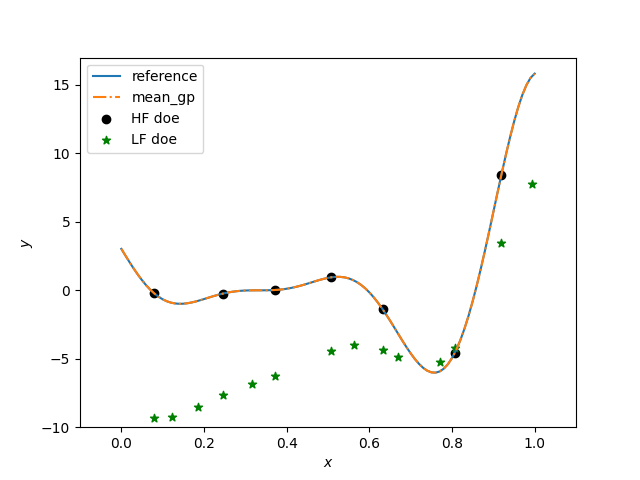
plt.figure()
plt.plot(x, hf_function(x), label="reference")
plt.plot(x, y, linestyle="-.", label="mean_gp")
plt.scatter(xt_e, yt_e, marker="o", color="k", label="HF doe")
plt.scatter(xt_c, yt_c, marker="*", color="g", label="LF doe")
plt.legend(loc=0)
plt.ylim(-10, 17)
plt.xlim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.xlabel(r"$x$")
plt.ylabel(r"$y$")
plt.show()
___________________________________________________________________________
MFKPLS
___________________________________________________________________________
Problem size
# training points. : 7
___________________________________________________________________________
Training
Training ...
Training - done. Time (sec): 0.0448298
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 101
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0002019
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000020
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 101
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0002139
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000021
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
print_global |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Global print toggle. If False, all printing is suppressed |
print_training |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print training information |
print_prediction |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print prediction information |
print_problem |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print problem information |
print_solver |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print solver information |
poly |
constant |
[‘constant’, ‘linear’, ‘quadratic’] |
[‘str’] |
Regression function type |
corr |
squar_exp |
[‘abs_exp’, ‘squar_exp’] |
[‘str’] |
Correlation function type |
pow_exp_power |
1.9 |
None |
[‘float’] |
Power for the pow_exp kernel function (valid values in (0.0, 2.0]), This option is set automatically when corr option is squar, abs, or matern. |
categorical_kernel |
MixIntKernelType.CONT_RELAX |
[<MixIntKernelType.CONT_RELAX: ‘CONT_RELAX’>, <MixIntKernelType.GOWER: ‘GOWER’>, <MixIntKernelType.EXP_HOMO_HSPHERE: ‘EXP_HOMO_HSPHERE’>, <MixIntKernelType.HOMO_HSPHERE: ‘HOMO_HSPHERE’>, <MixIntKernelType.COMPOUND_SYMMETRY: ‘COMPOUND_SYMMETRY’>] |
None |
The kernel to use for categorical inputs. Only for non continuous Kriging |
hierarchical_kernel |
MixHrcKernelType.ALG_KERNEL |
[<MixHrcKernelType.ALG_KERNEL: ‘ALG_KERNEL’>, <MixHrcKernelType.ARC_KERNEL: ‘ARC_KERNEL’>] |
None |
The kernel to use for mixed hierarchical inputs. Only for non continuous Kriging |
nugget |
2.220446049250313e-14 |
None |
[‘float’] |
a jitter for numerical stability |
theta0 |
[0.01] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
Initial hyperparameters |
theta_bounds |
[1e-06, 20.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
bounds for hyperparameters |
hyper_opt |
Cobyla |
[‘Cobyla’] |
[‘str’] |
Optimiser for hyperparameters optimisation |
eval_noise |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
noise evaluation flag |
noise0 |
[0.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
Initial noise hyperparameters |
noise_bounds |
[2.220446049250313e-14, 10000000000.0] |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
bounds for noise hyperparameters |
use_het_noise |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
heteroscedastic noise evaluation flag |
n_start |
10 |
None |
[‘int’] |
number of optimizer runs (multistart method) |
xlimits |
None |
None |
[‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
definition of a design space of float (continuous) variables: array-like of size nx x 2 (lower, upper bounds) |
design_space |
None |
None |
[‘BaseDesignSpace’, ‘list’, ‘ndarray’] |
definition of the (hierarchical) design space: use smt.utils.design_space.DesignSpace as the main API. Also accepts list of float variable bounds |
random_state |
41 |
None |
[‘NoneType’, ‘int’, ‘RandomState’] |
Numpy RandomState object or seed number which controls random draws for internal optim (set by default to get reproductibility) |
rho_regr |
constant |
[‘constant’, ‘linear’, ‘quadratic’] |
None |
Regression function type for rho |
optim_var |
False |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
If True, the variance at HF samples is forced to zero |
propagate_uncertainty |
True |
[True, False] |
[‘bool’] |
If True, the variance cotribution of lower fidelity levels are considered |
n_comp |
1 |
None |
[‘int’] |
Number of principal components |