Benchmarking problems¶
SMT contains a library of analytical and engineering problems to be used for benchmarking purposes. These are listed below.
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.problems import Sphere
ndim = 2
problem = Sphere(ndim=ndim)
num = 100
x = np.ones((num, ndim))
x[:, 0] = np.linspace(-10, 10.0, num)
x[:, 1] = 0.0
y = problem(x)
yd = np.empty((num, ndim))
for i in range(ndim):
yd[:, i] = problem(x, kx=i).flatten()
print(y.shape)
print(yd.shape)
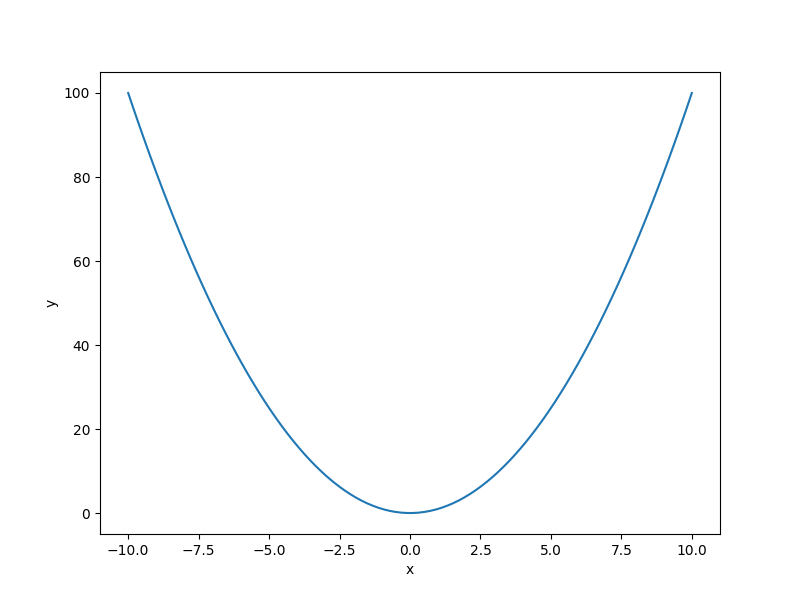
plt.plot(x[:, 0], y[:, 0])
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.show()
(100, 1)
(100, 2)
Problem class API¶
- class smt.problems.problem.Problem(**kwargs)[source]¶
- Attributes:
design_spaceGets the design space definitions as an instance of BaseDesignSpace
Methods
__call__(x[, kx])Evaluate the function.
sample
- __init__(**kwargs)[source]¶
Constructor where values of options can be passed in.
For the list of options, see the documentation for the problem being used.
- Parameters:
- **kwargsnamed arguments
Set of options that can be optionally set; each option must have been declared.
Examples
>>> from smt.problems import Sphere >>> prob = Sphere(ndim=3)
- __call__(x: ndarray, kx: int | None = None) ndarray[source]¶
Evaluate the function. The input vectors might be corrected if it is a hierarchical design space. You can get the corrected x and information about which variables are acting from: problem.eval_x and problem.eval_is_acting
- Parameters:
- xndarray[n, nx] or ndarray[n]
Evaluation points where n is the number of evaluation points.
- kxint or None
Index of derivative (0-based) to return values with respect to. None means return function value rather than derivative.
- Returns:
- ndarray[n, 1]
Functions values if kx=None or derivative values if kx is an int.