GENN¶
Gradient-Enhanced Neural Networks (GENN) are fully connected multi-layer perceptrons, whose training process is modified to predict partial derivatives accurately. This is accomplished by minimizing a modified version of the Least Squares Estimator (LSE) that accounts for Jacobian prediction error. The main benefit of jacobian-enhancement is better accuracy with fewer training points compared to standard fully connected neural nets. This surrogate model relies on an upstream library called jenn where more details on the implementation can be found.
Usage¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from smt.surrogate_models import GENN
# Test function
def f(x):
import numpy as np # need to repeat for sphinx_auto_embed
return x * np.sin(x)
def df_dx(x):
import numpy as np # need to repeat for sphinx_auto_embed
return np.sin(x) + x * np.cos(x)
# Domain
lb = -np.pi
ub = np.pi
# Training data
m = 4
xt = np.linspace(lb, ub, m)
yt = f(xt)
dyt_dxt = df_dx(xt)
# Validation data
xv = lb + np.random.rand(30, 1) * (ub - lb)
yv = f(xv)
dyv_dxv = df_dx(xv)
# Instantiate
genn = GENN()
# Likely the only options a user will interact with
genn.options["hidden_layer_sizes"] = [6, 6]
genn.options["alpha"] = 0.1
genn.options["lambd"] = 0.1
genn.options["gamma"] = 1.0 # 1 = gradient-enhanced on, 0 = gradient-enhanced off
genn.options["num_iterations"] = 500
genn.options["is_backtracking"] = True
# Train
genn.load_data(xt, yt, dyt_dxt)
genn.train()
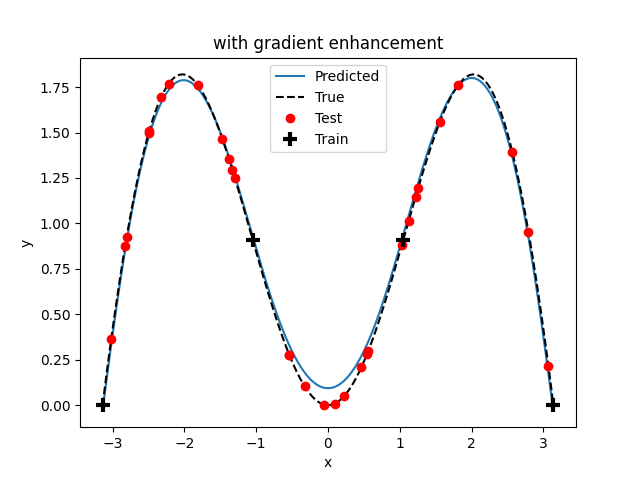
# Plot comparison
if genn.options["gamma"] == 1.0:
title = "with gradient enhancement"
else:
title = "without gradient enhancement"
x = np.arange(lb, ub, 0.01)
y = f(x)
y_pred = genn.predict_values(x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y_pred)
ax.plot(x, y, "k--")
ax.plot(xv, yv, "ro")
ax.plot(xt, yt, "k+", mew=3, ms=10)
ax.set(xlabel="x", ylabel="y", title=title)
ax.legend(["Predicted", "True", "Test", "Train"])
plt.show()
___________________________________________________________________________
GENN
___________________________________________________________________________
Problem size
# training points. : 4
___________________________________________________________________________
Training
Training ...
Training - done. Time (sec): 0.3032103
___________________________________________________________________________
Evaluation
# eval points. : 629
Predicting ...
Predicting - done. Time (sec): 0.0001469
Prediction time/pt. (sec) : 0.0000002
Options¶
Option |
Default |
Acceptable values |
Acceptable types |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
print_global |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Global print toggle. If False, all printing is suppressed |
print_training |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print training information |
print_prediction |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print prediction information |
print_problem |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print problem information |
print_solver |
True |
None |
[‘bool’] |
Whether to print solver information |
alpha |
0.05 |
None |
[‘int’, ‘float’] |
optimizer learning rate |
beta1 |
0.9 |
None |
[‘int’, ‘float’] |
Adam optimizer tuning parameter |
beta2 |
0.99 |
None |
[‘int’, ‘float’] |
Adam optimizer tuning parameter |
lambd |
0.01 |
None |
[‘int’, ‘float’] |
regularization coefficient |
gamma |
1.0 |
None |
[‘int’, ‘float’] |
gradient-enhancement coefficient |
hidden_layer_sizes |
[12, 12] |
None |
[‘list’] |
number of nodes per hidden layer |
mini_batch_size |
-1 |
None |
[‘int’] |
split data into batches of specified size |
num_epochs |
1 |
None |
[‘int’] |
number of random passes through the data |
num_iterations |
1000 |
None |
[‘int’] |
number of optimizer iterations per mini-batch |
seed |
-1 |
None |
[‘int’] |
random seed to control repeatability |
is_print |
False |
None |
[‘bool’] |
print progress (or not) |
is_normalize |
False |
None |
[‘bool’] |
normalize training by mean and variance |
is_backtracking |
False |
None |
[‘bool’] |
refine step step during line search (fixed otherwise) |